Aplikasi Kitosan berbasis Kulit Udang Sebagai Alternatif Subtitusi Lilin Pelapis dalam Rangka Peningkatan Umur Simpan Buah-Buahan: A Review
Main Article Content
Abstract
Sebagai negara dengan mayoritas penduduk beragama islam, pasar pangan di Indonesia sangat erat kaitannya dengan hukum halal haram. Salah satu pangan yang kerap dikonsumsi adalah buah-buahan, namun dengan karakternya yang mudah rusak dan membusuk, diperlukan suatu pelapis yang berperan sebagai pengawet untuk memperpanjang usia simpan buah-buahan tersebut termasuk dengan melapisi menggunakan lilin pelapis. Lilin pelapis dapat membahayakan tubuh jika dikonsumsi terus menerus sehingga tidak memenuhi syarat thayyib. Kitosan dari kulit udang dapat menjadi alternatif pengganti lilin pelapis karena dibuat dari bahan halal dan aman bagi tubuh. Kitosan dapat diproduksi secara enzimatis dan kimiawi. Proses pengkajian halal telah dilakukan baik dengan metode produksi secara enzimatik maupun kimiawi dimana keduanya memiliki beberapa titik kritis pada bahan yang digunakan yaitu pada komposisi bahan media untuk fermentasi untuk proses enzimatik dan pada penggunaan ionic liquids beserta etanol untuk proses kimiawi.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors who publish their manuscripts in this journal agree to the following terms:
- The copyright of each article remains with the authors.
- Halal Research Journal holds the right to publish the article first under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors may distribute their published manuscripts non-exclusively (e.g., to institutional repositories or as part of book publications), provided they acknowledge that the article was first published in this journal.
License
Articles published in this journal are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. This license permits anyone to:
- Copy, distribute, adapt, modify, and create derivative works from the material in any form, including for commercial purposes.
- The condition is that proper credit must be given to the authors for the original work.
References
Dukcapil, “273 Juta Penduduk Indonesia Terupdate Versi Kemendagri,” 2022.
Dwiari, Teknologi Pangan Jilid I untuk SMK. Jakarta: Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2008.
and A. W. Tanbury, Peter F., Principles of Fermentation Technology. New York: Pergamon Press, 1984.
G. T. Rekso, Pemanfaatan Limbah Perikanan. Jakarta: Puslitbang Teknologi Isotop dan Radiasi (P3TIR), Badan Teknologi Nasional, 2001.
Winarno FG, Kimia Pangan dan Gizi. Jakarta (ID): Gramedia Pustakatama, 2002.
and P. C. Pantastico ErB, Matto AK, Fisiologi pascapanen, penanganan dan pemanfaatan buah-buahan dan sayur-sayuran tropika dan sub tropika. Yogyakarta, Indonesia: Universitas Gadjah Mada, 1989.
Santoso BB dan Purwoko BS, Fisiologi dan Teknologi Pasca Panen Tanaman Hortikultura. Indonesia Australia Eastern Universities Project, 1995.
Kartasapoetra AG, Teknologi Penanganan Pasca Panen. Jakarta, Indonesia: Rineka Cipta, 1994.
J. K. Brecht, “Physiology of Lightly Processed Fruits and Vegetables,” HortScience, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 18–22, 1995, doi: 10.21273/hortsci.30.1.22.
P. N. Kumar, N. Jagathjothi, R. Ramasamy, dan S. Suresh, “Importance of Edible wax coatings in fruits and vegetables,” no. November, pp. 1–5, 2020.
H. P. Sharma, V. Chaudhary, dan M. Kumar, “Importance of edible coating on fruits and vegetables: A review,” ~ 4104 ~ J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem., vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 4104–4110, 2019.
S. Susanto, D. Inkorisa, dan D. Hermansyah, “Pelilinan Efektif Memperpanjang Masa Simpan Buah Jambu Biji (Psidium guajava L.) ‘Kristal,’” J. Hortik. Indones., vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 19–26, 2018, doi: 10.29244/jhi.9.1.19-26.
R. L. Bhardwaj, Y. K. Sharma, dan L. Vyas, Postharvest Handling of Horticultural Crops. CRC Press, 2021.
A. Gennadios dan W. C.L., “Edible Film and Coating From Wheat and Corn Protein,” J.Food echnol, vol. 44, no. 10, p. 63, 1990.
J. Kester dan O. Fennema, “Edible films and coatings: A review,” Food Technol., pp. 47–59, 1986.
F. Debeaufort, G. Quezada, dan A. Voilley, “Edible films and coating: Tomorrow’s packaging: A review,” Food Sc. Nutr., vol. 38, pp. 299–313, 1998.
E. Garcia dan D. Barret, “Preservative treatments for fresh cut fruits and vegetables,” in Fresh-Cut Fruits and Vegetables, O. Lamikan., CRC Press, 2002.
R. Contreras-Medellin dan T. Labuza, “Prediction of moisture protection requirements for foods,” Cereal Food World, vol. 26, no. 7, pp. 335–343, 1981.
M. V, D. F, B. G, C. M, dan V. A, “Factors affecting the moisture permeability of lipid-based edible films: A review,” Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr., vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 67–89, 2002.
B. EA, K. JM, dan N. MO, “Edible coatings and films to improve food quality,” in Edible coatings for fresh fruits and vegetables: past, present, and future, CMC Press, 1994, pp. 25–64.
G. IK dan F. O, “Lipid-based edible films and coatings,” Lipid Tech, vol. 4, pp. 34–38, 1992.
L. D dan Z. Y, “Innovation the development and application of edible coating for fresh and minimally processed fruits and vegetables,” Food Sc. Food Saf., vol. 6, pp. 60–75, 2007.
M. R dan S. P, “Mechanical property of and water vapour transferability through whey protein film,” J Dairy Sc, vol. 75, pp. 942–946, 1992.
R. Pratiwi, “Manfaat kitin dan kitosan bagi kehidupan manusia,” Oseana, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 35–43, 2014.
C. Purnawan, N. H. A, I. Kartini, dan E. Suguharto, “MENGGUNAKAN THERMOGRAVIMETRIC ANALYSIS DAN DIFFERENTIAL THERMAL ANALYSIS ( TGA-DTA ) Kajian Analisis Termal … ( Candra , dkk ),” J. Ris. Kim., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 44–52, 2008.
Zulfahmi dan M. R. S. Taufan, “Pemanfaatan Limbah Kulit Udang sebagai Bahan Anti Rayap ( Bio-termitisida ) pada Bangunan Berbahan Kayu,” Skripsi, Univ. Diponegoro, p. 44, 2010.
R. A. Muzzarelli, Chitin In The Polysaccharisses, 3rd ed. New York: Academic Press, 1985.
I. M. Ridwan, S. Mus, dan R. Karnila, “Pengaruh Edible Coating dari Kitosan Terhadap Mutu Fillet Ikan Nila (Oreochromis niloticus) yang Disimpan pada Suhu Rendah,” Jom, vol. 1, no. 10, pp. 1–15, 2015.
B. W. Sari, I. Nurul B, P. Indun D., H. Amir, dan Ustadi, “Pembentukan N-Asetilglukosamin dari Kitin Cangkang Udang oleh Serratia marcescens PT-6 yang d ikultur pada b erbagai pH dan Suhu Bioformation of N-Acetylglucosamine from Shrimp Shell Chitin by Serratia marcescens PT-6 Cultured in v arious pH and Temperatu,” Perikan. Univ. Gajah Mada, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 53–59, 2017.
S. Agustina, I. Swantara, dan I. Suartha, “Isolasi Kitin, Karakterisasi, Dan Sintesis Kitosan Dari Kulit Udang,” J. Kim., vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 271–278, 2015.
S. Lee, J.-S. Cho, dan G. Cho, “Antimicrobial and Blood Repellent Finishes for Cotton and Nonwoven Fabrics Based on Chitosan and Fluoropolymers,” Text. Res. J., vol. 69, no. 2, pp. 104–112, Feb. 1999, doi: 10.1177/004051759906900205.
M. R. A. Thariq, A. Fadli, A. Rahmat, dan R. Handayani, “Pengembangan Kitosan Terkini pada Berbagai Aplikasi Kehidupan: Review," J. Teknol. Pangan, no. October, p. Hal. 49-57, 2016, [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311806381.
A. Tolaimate, J. Desbrieres, M. Rhazi, dan A. Alagui, “Contribution to the preparation of chitins and chitosans with controlled physico-chemical properties,” Polymer (Guildf)., vol. 44, no. 26, pp. 7939–7952, 2003, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2003.10.025.
L. M. Champagne, “The Synthesis of Water Soluble N-Acyl Chitosan Derivatives for Characterization As Antibacterial Agents,” LSU Dr. Diss., no. May, pp. 1–126, 2008, [Online]. Available: https://digitalcommons.lsu.edu/gradschool_dissertations/2289.
Y.-S. Oh, I.-L. Shih, Y.-M. Tzeng, dan S.-L. Wang, “Protease produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa K-187 and its application in the deproteinization of shrimp and crab Shell wastes,” Enzyme Microb. Technol., vol. 27, pp. 3–10, Aug. 2000, doi: 10.1016/S0141-0229(99)00172-6.
H. Muhammad, “PENYEDIAAN CARBOXYMETHYL CELLULOCE (CMC) DARI TEPUNG BIJI DURIAN SEBAGAI PENGENTAL FOOD GRADE DENGAN METODE GERMAN BATCH PROCESS,” Universitas Sumatera Utara, 2021.
M. R. A. Thariq, A. Fadli, A. Rahmat, dan R. Handayani, “Pengembangan Kitosan Terkini pada Berbagai Aplikasi Kehidupan: Review," J. Teknol. Pangan, no. October, p. Hal. 49-57, 2016, [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311806381.
S. R. Fatihiyah, “Deproteinasi Kulit Udang Secara Fermentasi Menggunakan Isolat Bacillus licheniformis F11 Pada Ekstrasi Kitin,” Inst. Pertan. Bogor, 2006.
W.-J. Jung, G. H. Jo, J. H. Kuk, Y. J. Kim, K. T. Oh, dan R.-D. Park, “Production of chitin from red crab shell waste by successive fermentation with Lactobacillus paracasei KCTC-3074 and Serratia marcescens FS-3,” Carbohydr. Polym., vol. 68, pp. 746–750, Apr. 2007, doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.08.011.
L. O. A. . Ramadhan, C. L. Radiman, D. Wahyuningrum, V. Suendo, L. O. Ahmad, and S. Valiyaveetiil, “Deasetilasi Kitin secara Bertahap dan Pengaruhnya terhadap Derajat Deasetilasi serta Massa molekul Kitosan,” J. Kim. Indones., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 17–21, 2010.
MUI, “Kriteria Sistem Jaminan Halal dalam HAS23000,” 2021. .
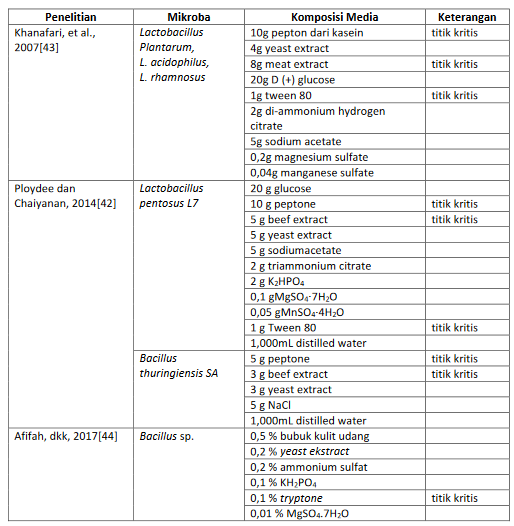
E. Ploydee dan S. Chaiyanan, “Production of high viscosity chitosan from biologically purified chitin isolated by microbial fermentation and deproteinization,” Int. J. Polym. Sci., vol. 2014, 2014, doi: 10.1155/2014/162173.
A. Khanafari, R. Marandi, dan S. Sanatei, “Recovery of chitin and chitosan from shrimp waste by chemical and microbial methods,” Iran. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 19–24, 2008.
K. N. Afifah, M. P. Koentjoro, dan E. N. Prasetyo, “Produksi Kitosan Secara Enzimatik oleh Bacillus Sampah Perikanan Enzymatic Chitosan Production by New Isolated Bacillus from Fisheries Waste,” vol. 14, pp. 286–294, 2017.
Y. Saleh, A. Nasr, H. Zaki, M. Mohamed, dan N. Kandile, “Extraction and Characterization of Chitosan from Shrimp Shells (Egypt: case study)," J. Sci. Res. Sci., vol. 33, no. part1, pp. 396–407, 2018, doi: 10.21608/jsrs.2016.17145.
L. D. Tolesa, B. S. Gupta, dan M. J. Lee, “Chitin and chitosan production from shrimp shells using ammonium-based ionic liquids,” Int. J. Biol. Macromol., vol. 130, pp. 818–826, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.018.
R. S. C. M. D. Q. Antonino et al., “Preparation and characterization of chitosan obtained from shells of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei Boone),” Mar. Drugs, vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 1–12, 2017, doi: 10.3390/md15050141.